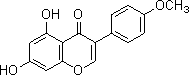
Product Name : Biochanin A
Synonyms : Biochanin A; 4’-methylgenistein; 5,7-dihydroxy-4’-methoxyisoflavone;
5,7-Dihydroxy-4′-methoxyisoflavone; Genistein 4′-methyl ether;
CAS No. : 491-80-5
Mol. Formula : C16H12O5
Mol. Weight : 284.26
Botanical Source : Red Clover (Trifolium pratense); Chick-Pea
Catalogue No. : B09019
Purity : >98% by HPLC
Packaging : 20mg, 50mg,100mg,1g,10g,100g...kgs
Package and quantity according to customer's detail requirement.
Remark : In stock, customized for large scale.
DESCRIPTION :
Biochanin A belongs to the isoflavone class of flavonoids. It is also classified as a phytoestrogen since it is a plant-derived nonsteroidal compound that possesses estrogen-like biological activity. Biochanin A has been found to have weak estrogenic activity.
Biochanin A is found in certain legumes, most notably red clover or Trifolium pratense. Red clover contains, in addition to biochanin A, the isoflavones genistein, daidzein and formononetin (methoxy daidzein). These isoflavones are present in red clover in the form of glycosides. However, when the leaves are crushed during the preparation of red clover isoflavone extracts, the glycosides undergo enzymatic hydrolysis, and the final preparation principally contains the aglycones.
ACTIONS AND PHARMACOLOGY
ACTIONS
Biochanin A has estrogenic activity. It may also have antioxidant, anticarcinogenic, anti-atherogenic and anti-osteoporotic activities.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Biochanin A has weak estrogenic activity as measured in in vivo and in vitro assays.
Structurally, biochanin A would be expected to be able to scavenge reactive oxygen species and inhibit lipid peroxidation. However, there are few studies demonstrating this.
There are cell culture and animal studies indicating that biochanin A has anticarcinogenic activity. It is unclear what the mechanism of the possible anticarcinogenic activity might be.
Biochanin A has been found to have hypolipidemic activity in some animal models. Again the mechanism of this possible effect, as well as the mechanism of any anti-atherogenic activity, is unclear.
In comparison with other isoflavones, such as genistein and daidzein, biochanin A might be expected to have possible anti-osteoporotic activity. This might be due, in part, to its weak estrogenic activity.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Little is known about the pharmacokinetics of biochanin A in humans. Inferences can be drawn from some animal studies. Biochanin A appears to be absorbed from the small intestine from whence it is transported to the systemic circulation by the lymphatics. There is little information available on the tissue distribution of biochanin A. It appears that biochanin A delivered to the liver undergoes extensive conjugation with glucuronate and sulfate via hepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferases and sulfotransferases. The glucuronate and sulfate conjugates of biochanin A are excreted in the urine and the bile.
It is likely that there is considerable variation in the absorption and metabolism of ingested biochanin A.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
There is very preliminary evidence that biochanin A may have some anti-atherosclerotic and anticarcinogenic effects. There are anecdotal reports that it may be helpful in ameliorating some of the problems associated with menopause, including osteoporosis.
RESEARCH SUMMARY
Biochanin A significantly reduced the incidence of chemically induced rat mammary cancer in a recent study. Multiplicity of tumors was also significantly decreased in biochanin A-supplemented animals, compared with unsupplemented controls. There is, additionally, some preliminary evidence that biochanin A may have some hypolipidemic effects. Clinical studies are lacking.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Biochanin A-containing supplements are derived from red clover and, in addition to biochanin A, usually contain the isoflavones genistein, daidzein and formononetin. A typical dose of such an isoflavone mixture—which also contains ingredients other than isoflavones—is 40 mg daily.
Reference :
1,Gotoh T, Yamada K, Yin H, et al. Chemoprevention of N-nitroso-N-methylurea-induced rat mammary carcinogenesis by soy foods or biochanin A. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1998; 89:137-142.
2,Lee YS, Kim TH, Cho KJ, Jang JJ. Inhibitory effects of biochanin A on benzo[a]pyrene induced carcinogenesis in mice. In vivo. 1992; 6:283-286.
3,Saloniemi H, Wà hà là K, Nykà nen-Kurki P, et al. Phytoestrogen content and estrogenic effect of legume fodder. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1995; 208; 13-17.
4,Siddiqui MT, Siddiqui M. Hypolipidemic principles of Cicer Arietnum: biochanin A and formononetin. Lipids. 1976; 11:243-246.
5,Yanagihara K, Ito A, Toge T, Numoto M. Antiproliferative effects of isoflavones on human cancer cell lines established from the gastrointestinal tract. Cancer Res. 1993; 53:5815-5821.