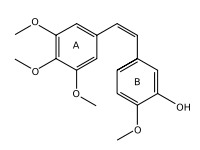
Product name : Combretastatin
Synonyms : Combretastatin A-4; Combretastatin A4; Combrestatin A4; CA4; CRC 87-09; NSC 817373; 2-Methoxy-5-[(1Z)-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenol
Mol. Formula : C18H20O5
Mol. Weight : 318.3643
CAS No. : 117048-59-6
Catalogue No. : C09009
Purity : > 98%,99% by HPLC
Package : 20mg, 50mg, 100mg, 1g,10g, 100g...
Package and quantity according to customer's detail requirement.
Remark : In stock, customized for large scale.
We can also suplly CA4P, combretastatin A4 phosphate.
The combretastatins are a class of natural stilbenoid phenols. A variety of different natural combretastatin molecules are present in the bark of Combretum caffrum, commonly known as South African Bush Willow. Despite having a similar name combretastatin is unrelated to statins, a family of cholesterol lowering drugs.
Natural combretastatins :
Molecules that fall into the combretastatin family generally share 3 common structural features: a trimethoxy 'A'-ring, a 'B'-ring containing substitutents often at C3' and C4', and an ethene bridge between the two rings which provides necessary structural rigidity. Molecules with C3' amino and hydroxyl substituents are very active, and molecules with C4' hydroxyl or methoxy substituents are also cytotoxic. Of the natural products presently known combretastatin A-4 is the most potent in regards to both tubulin binding ability and cytotoxicity. Combretastatin A-1 is also a potent cytotoxic agent.
Biological function :
Members of the combretastatin family possess varying ability to cause vascular disruption in tumors. Combretastatin binds to the β-subunit of tubulin at what is called the colchicine site, referring to the previously discovered vascular disrupting agent colchicine. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization prevents cancer cells from producing microtubules. Microtubules are essential to cytoskeleton production, intercellular movement, cell movement, and formation of the mitotic spindle used in chromosome segregation and cellular division. The anti-cancer activity from this action results from a change in shape in vasculature endothelial cells. Endothelial cells treated with combretastatin rapidly balloon in shape causing a variety of effects which result in necrosis of the tumor core. The tumor edge is supported by normal vasculature and remains, for the most part, unaffected. As a result it is likely that any therapeutic use will involve a combination of drugs or treatment options.
Clinical studies :
Combretastatin A-4, the most potent naturally occurring combretastatin known, its phosphate prodrug (CA-4-P), and multiple other analogs of CA-4 are currently being investigated in a number of clinical trials. In July 2007 the pharmaceutical company OXiGENE initiated a 180-patient phase III clinical trial of CA-4-P in combination with carboplatin for the treatment of anaplastic thyroid cancer (Study of Combretastatin and Paclitaxel/Carboplatin in the Treatment of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer). There is currently no fully FDA approved treatment for this form of cancer.
References :
1,Pettit, G. R. Sheo Bux Singh Boyd, M. R. Hamel, E. (1995), 'Antineoplastic Agents. 291. Isolation and Synthesis of Combretastatins A-4, A-5, and A-6', Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 38: 1666-1672 2,Nam, N. Combretastatin A-4 Analogues as Antimitotic Antitumor Agents Current Medicinal Chemistry, 2003, 10, 1697-1722.
3,Sackett, D; Varma, J. Molecular mechanism of Colchicine action: induced local unfolding of beta tubulin Biochemistry, 1993, 32, 13560-13565.
4,Beauregard, D; Hill, S; Chaplin, D; Brindle, K. The susceptibility of tumors to the antivascular drug combretastatin A4 phosphate correlated with vascular permeability Cancer Research, 2001, 61, 6811-6815.
5,Griggs, J; Metcalfe, J. C; Hesketh, R. Targeting tumor vasculature: the development of combretastatin A4 Lancet Oncol, 2001, 2, 82-87.
6,Hadfield, J; Ducki, S; Hirts, N; McGown, A. Tubulin and microtubules as targets for anticancer drugs Progress in Cell Cycle Research, 2003, 5, 309-325.
7,Hinnen, P. 'Vascular disrupting agents in clinical development' British Journal of Cancer (2007) 96, 1159-1165.
8,Hori, K; Saito, S. Microvascular Mechanisms by which the Combretastatin A-4 Derivative AC7700 (AVE8062) Induces Tumor Blood Flow Stasis British Journal of Cancer, 2003, 89, 1334-1344.
9,Jordan, Mary Ann 'Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs' Nature Reviews Cancer, 2004, 4, 253-265
10,Tozer, G. 'Disrupting tumour blood vessels' Nature Reviews Cancer, 2005, 5, 432-435
11,Tron, G; Pirali, T; Sorba, G; Pagliai, F; Busacca, S; Genazzani, A. Medicinal Chemistry of Combretastatin A4: Present and Future Directions Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2006, 49, 3033-3044.
12,Pandit, Bulbul; Sun, Yanjun; Chen, Ping; Sackett, Dan; Hu, Zhigen; et al. Structure-activity-relationship studies of conformationally restricted analogs of combretastatin A-4 derived from SU5416 Bioorganic and Medicinal Chem, 2006, 14, 6492-6501
13,Pati, H; Taherbhai, Z; Forrest, L; Wicks, M; Bailey, S; Staples, A; et al. A Stereospecific Route for the Preparation of Trans-Combretastatin Analogs: Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Letters in Drug Design & Discovery, 2004, 1, 275-278.
14,Patterson, D. “Vascular Damaging Agents” Clinical Oncology, 2007, 19, 443-456
15,Salmon, B. “Characterizing the Tumor Response to Treatment with Combretastatin A-4 Phosphate” Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys, 2007, 68, 1, 211-217